From the nearly ~650 filings our Robo-Analyst analyzed last week, we’re highlighting unusual items in the filings of Exxon Mobil (XOM) and several other companies during the second week of The Real Earnings Season.
Exxon’s Hidden Non-Operating Items Significantly Impact Earnings
In its 2020 10-K, analyst Jacob McDonough found that Exxon Mobil recorded multiple write-downs that were hidden in “Depreciation and depletion” and “Exploration expenses, including dry holes.” Detailed below, these hidden and reported unusual gains/losses amount to $22.5 billion and materially distort (by 100%) Exxon’s GAAP earnings:
- $24 billion charge in Upstream to reduce carrying value of the dry gas portfolio to fair value – Page 80 2020 10-K
- $1.2 billion non-service pension and postretirement benefit expense reported on the income statement
- $900 million impairment charge in the Upstream unit – Page 80 2020 10-K
- $611 million pre-tax goodwill impairment charges in the Upstream, Downstream, and Chemical units – Page 75 2020 10-K
- $600 million impairment related to U.S. upstream equity investments – Page 78 2020 10-K
- $500 million impairment charge in the Downstream unit – Page 80 2020 10-K
- $450 million pre-tax charges related to employee separation costs – Page 107 2020 10-K
- $100 million impairment charge in the Chemical unit – Page 80 2020 10-K
- $73 million amortization of prior service costs – Page 96 2020 10-K
In addition, we made a $5.4 billion adjustment for income tax distortion to normalize reported income taxes by removing the impact of unusual items.
In total, Exxon has -$22.5 billion in Earnings Distortion that reduces earnings by -$5.26/share, or 100% of GAAP EPS. After removing Earnings Distortion, Exxon’s 2020 Core Earnings of $0.01/share are much greater than GAAP EPS of -$5.25.
How We Treat Non-Operating Items: Non-operating items, such as asset write-downs, restructuring, or litigation costs, are one of many reasons why GAAP net income doesn’t tell the whole story of a company’s profitability.
We remove all unusual gains/losses, including write-downs, to calculate Exxon’s true recurring profits, i.e. Core Earnings. We also add-back the after-tax value of asset write-downs to our measure of invested capital to ensure management can’t erase equity from the balance sheet.
Without careful footnotes research, investors would never know that these non-recurring expenses distort GAAP numbers to the point where traditional, unscrubbed earnings for U.S. stocks are off by an average of ~20%.
Other Material Earnings Distortions & Red Flags We Found
Since February 19, 2021, we have parsed 1,395 10-Q and 10-K filings, which means Exxon’s hidden non-operating items aren’t the only unusual items our analysts have found. Below are a few other highly material Earnings Distortions that we discovered while rigorously analyzing the footnotes and MD&A:
Chegg, Inc. (CHGG) – Abnormal reported tax rate
- While analyzing Chegg’s 2020 10-K, analyst Alex Sword found a notable tax situation. On page 82 of its 2020 10-K, the firm discloses a 2,900% tax expense for stock-based compensation and a 5,900% tax benefit from convertible senior notes. Ultimately, despite reporting a GAAP pre-tax loss of $861,000, Chegg reported over $5 million in taxes during 2020. However, we made a $5 million adjustment for income tax distortion to normalize reported income taxes by removing the impact of unusual items. After removing all Earnings Distortion (177% of GAAP EPS in 2020), Chegg’s 2020 Core Earnings of $0.04/share are much greater than GAAP EPS of -$0.05.
S&T Bancorp, Inc. (STBA) – Non-operating loss due to fraud
- Analyst Devyn DeLange noticed on page 111 of S&T Bancorp’s 2020 10-K that the firm recognized a $59 million pre-tax loss due to fraud resulting from a check kiting scheme. We remove this non-operating charge from our measure of net operating profit after tax (NOPAT) and Core Earnings to calculate the true recurring profits of the business. After removing all Earnings Distortion (275% of GAAP EPS in 2020), S&T Bancorp’s 2020 Core Earnings of $2.01/share are greater than GAAP EPS of $0.54.
Orthofix Medical, Inc. (OFIX) – Related party transaction with possible conflict of interest
- Analyst Sam Moorhead found the disclosure of a related party transaction that could create a conflict of interest on page F-43 of Orthofix Medical’s 2020 10-K. Per the disclosure, Orthofix entered into a technology assignment and royalty agreement with a medical device technology company partially owned and controlled by the wife of Orthofix’s President and Chief Executive Officer for consideration up to $10 million. While the firm noted the CEO was excluded from the negotiation and evaluation of the transaction, such a finding is a good reminder that potential conflicts of interest may only be disclosed deep within annual filings. Diligence matters.
The Power of the Robo-Analyst
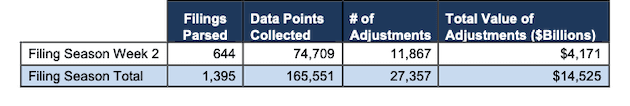
We analyzed 644 10-K and 10-Q filings last week, from which our Robo-Analyst[1] technology collected 74,709 data points. Our analyst team made 11,867 forensic accounting adjustments with a dollar value of $4.2 trillion. The adjustments were applied as follows:
- 4,408 income statement adjustments with a total value of $340 billion
- 4,891 balance sheet adjustments with a total value of $1.7 trillion
- 2,568 valuation adjustments with a total value of $2.1 trillion.
Figure 1: Filing Season Diligence for the Week of March 1 – March 5
Sources: New Constructs, LLC and company filings.
Every year in this six-week stretch from mid-February through the end of March, we parse and analyze roughly 2,000 10-Ks to update our models for companies with 12/31 and 1/31 fiscal year ends. This effort is made possible by the combination of expertly trained human analysts with our “Robo-Analyst.” Featured by Harvard Business School in “Disrupting Fundamental Analysis with Robo-Analysts”, our Robo-Analyst research automation technology uses machine learning and natural language processing to automate and improve financial modeling.
Only our “novel dataset”, which leverages our Robo-Analyst technology, enables investors to overcome flaws with legacy fundamental datasets to apply reliable fundamental data in their research. Core Earnings: New Data & Evidence, forthcoming in The Journal of Financial Economics, reveals the problems with fundamental data provided by legacy firms like Bloomberg, Refinitiv, FactSet (FDS) and S&P Global (SPGI).
This article originally published on March 9, 2021.
Disclosure: David Trainer, Jacob McDonough, Alex Sword, Devyn DeLange, Sam Moorhead, Kyle Guske II, and Matt Shuler receive no compensation to write about any specific stock, sector, style, or theme.
Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and StockTwits for real-time alerts on all our research.
[1] Harvard Business School features the powerful impact of our research automation technology in the case New Constructs: Disrupting Fundamental Analysis with Robo-Analysts.